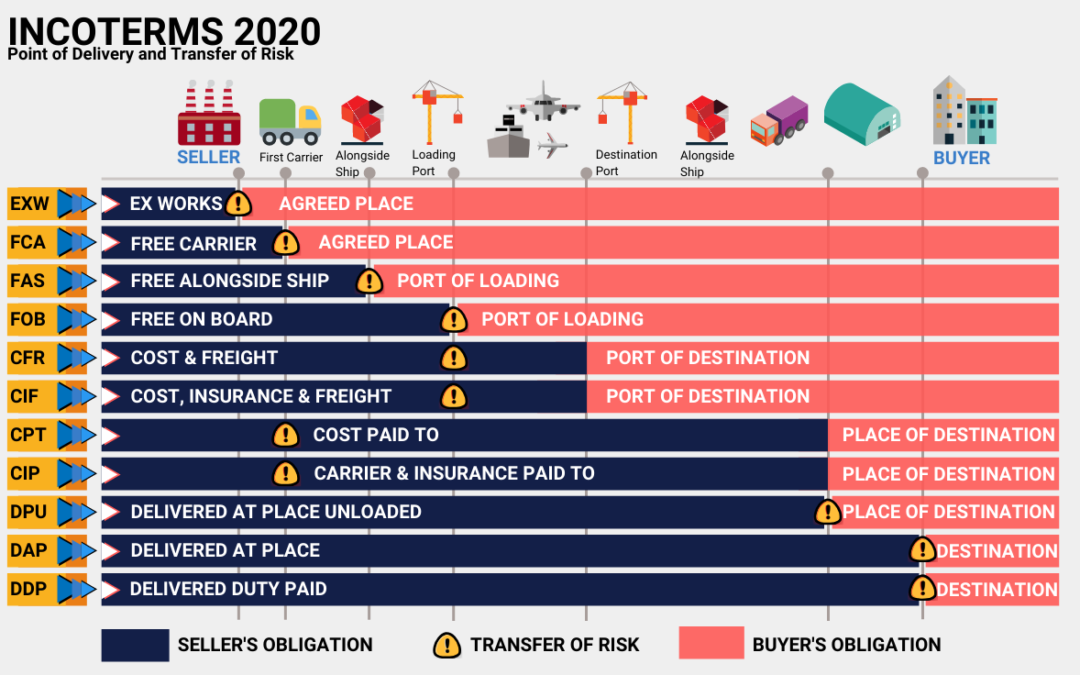
INCOTERMS® 2020
Each individual coded abbreviation in the Incoterms, clearly defines who should bear the costs and responsibilities for each part of the transport, for the customs costs at departure and arrival, for the insurance costs.
EXW (EX Works)
The seller simply has to prepare the goods on his premises (factory, warehouse, etc.) on the agreed date, providing only for the provision of documentation suitable for export from the country of origin.
The buyer, for his part, will have to arrange the export customs operation (if he is unable to do so, the return will have to be changed in FCA), will organize the transport and pay all the costs, also taking all the risks up to the final destination.
FCA (Free Carrier)
The seller must prepare the goods on the agreed date, providing the documentation suitable for export from the country of origin, delivery to the warehouse of the shipper (or other person chosen by the buyer) and payment of the costs related to the operation. export customs.
The buyer, for his part, will arrange the transport from that place and pay all the costs, also taking all the risks up to the final destination.
CPT (Carriage Paid To)
TRANSPORT PAID UP TO “Transport paid to” means that the seller delivers the goods by handing the goods back to the carrier or another person designated by the same seller at an agreed place (if such place has been agreed between the parties) and that the seller must stipulate the transport contract and bear the necessary costs for sending the goods to the place of agreed destination. The seller fulfills his obligation to deliver when he returns the goods to the carrier and not when the goods arrive at the place of destination. CPT requires the seller, if necessary, to clear the goods for export.
CIP (Carriage & Insurance Paid)
TRANSPORT AND INSURANCE PAID UNTIL A. The seller is responsible for all transport costs up to a specified point of arrival, as well as the costs for obtaining licenses and documentation for export from the country of origin and those for customs operations always export and insurance. The costs to be incurred for crossing other countries to the point of arrival are also supported by the sender.
DAT (Delivered at Terminal)
RETURN TO TERMINAL. The seller makes the delivery by placing the goods, once unloaded from the means of transport of arrival, available to the buyer at the agreed terminal in the agreed port or place of destination. “Terminal” includes any place, covered or uncovered, such as a quay, warehouse, container yard, road, rail or airport terminal.
The seller bears all the concerning risks with the transport and unloading of the goods at the terminal in the agreed port or place of destination.
DAP (Delivered at Place)
RETURNED TO PLACE OF DESTINATION. The seller makes the delivery by placing the goods at the disposal of the buyer on the means of transport of arrival ready for unloading at the agreed destination.
The seller bears all the risks associated with the transport of the goods to the agreed place.
DDP (Delivered Duty Paid)
The seller delivers the goods by placing the goods at the disposal of the buyer, cleared for importation, on the means of transport of arrival ready for unloading at the agreed destination. The seller bears all the costs and concerning risks with the transport of the goods to the place of destination and he is obliged to clear the goods not only for export but also for import, to pay any export and import duties and complete all customs formalities.
Rules for maritime transport and inland waterways
FAS (Free Alongside Ship)
The seller carries out the delivery by placing the goods alongside the ship (eg on a quay or barge) designated by the buyer in the named port of shipment. The risk of loss or damage to the goods is when the goods are alongside the ship and the buyer bears all costs from that moment on. The parties are recommended to specify as clearly as possible the loading point in the named port of shipment, as the costs and risks up to that point are borne by the seller and these expenses and the associated handling charges may change depending on the uses of the port. If the goods are containerized, it is customary for the seller to deliver the goods to the carrier at the terminal and not alongside the ship.
FOB (Free on Board)
The seller carries out the delivery by placing the goods on board the ship designated by the buyer in the agreed port of shipment or by procuring the goods already delivered in this way. The risk of loss or damage to the goods is when the goods are on board the ship and the buyer bears all costs from that moment on. FOB requires that the seller, if applicable, clears the goods for export.
CFR (Cost & Freight)
The seller is responsible for all transport costs to destination, as well as the costs for obtaining licenses and documentation for export from the country of origin and for customs operations, always for export.
The buyer is responsible for the insurance costs (all data must be promptly communicated by the seller) and all other costs from the port of arrival, including customs costs in the country of arrival.
CIF (Cost Insurance & Freight)
The seller delivers by placing the goods on board the ship or by procuring the goods already delivered. The risk of loss or damage to the goods is when the goods are on board the ship.
The seller must issue the transport contract and bear the costs necessary for sending the goods to the agreed port of destination. The seller also provides insurance coverage against the buyer’s risk of loss or damage to the goods during transport.


